In Silico Design and Screening of Cephalosporin Derivatives for Their Inhibitory Potential Against Haemophilus influenza
by Chikame Dawa Sangma, Dipak Chetia, Malita Sarma Borthakur, Lima Patowary, Dubom Tayeng ★
Academic editor: James H. Zothantluanga
Sciences of Phytochemistry 1(2): 60-67 (2022); https://doi.org/10.58920/sciphy01020001
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) 4.0 International License.
23 Aug 2022
12 Oct 2022
12 Oct 2022
12 Oct 2022
Abstract: Antibiotics kill bacteria by blocking essential metabolic processes which prevent them from reproducing thereby allowing the immune system to fight bacterial infections. However, the emergence and the quick spread of bacterial resistance against clinically approved antibiotics have become alarming. This necessitates the development of novel treatment options and alternative antimicrobial therapies in the fight against bacterial infections. In this study, we aim to virtually design and carry out in silico studies to identify a cephalosporin derivative with inhibitory potential against Haemophilus influenza. Data Warrior software, Discovery studio software, PyRx tool, Swiss ADME web tool, and ProTox-II web tool were used to screen the cephalosporin derivatives. Initially, 17 cephalosporin derivatives were preliminarily screened for their toxicity followed by in silico ADME studies. Among the cephalosporin derivatives, C1, C6, and C12 were found to be the potential drug-like molecules with binding energies of -7.4 kcal/mol, -7.1 kcal/mol, and -7.1 kcal/mol, respectively. In particular, C1 was predicted to have a moderate biological activity with a high bioavailability score. Based on the ADME profile, toxicity, binding energy, drug-likeness, and drug score, we conclude C1 (‘F’ at the 3rd position) as the potential lead molecule to inhibit H. influenza.
Keywords: In-silicoCephalosporinsAntibioticsDrug resistanceHaemophilus influenza
Introduction
Antibiotics are substances that kill or inhibit the growth of living organisms. Antibiotics operate by killing bacteria, blocking essential bacterial processes, preventing them from proliferating, and allowing the immune system to fight bacterial infection (1). Antibiotics have been used in the health care system for many years and recently, it was found that some bacterial infections were resistant to the current antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance is a major global problem as it is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates (2). Resistance of bacterial pathogens to multiple antimicrobial therapies is increasing at an alarming rate and this is known as multidrug resistance. Antibiotic resistance rises rapidly with poor infection control practices and these resistant bacteria spread easily to other patients (3). The current shortage of effective drugs, lack of successful prevention measures, and only a few new antibiotics in the clinical pipeline have necessitated the need to develop novel treatment options to fight drug-resistant bacteria (3).
Cephalosporins (Figure 1) belonged to the class of broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics. They have been in clinical use since their discovery during the 1960s. In comparison to other drugs, cephalosporins have a low rate of drug-related adverse effects and their pharmacokinetic characteristics are favorable. Cephalosporins are commonly utilized as the first-line treatment for pneumonia, meningitis, gonorrhea, and other microbial infections (4). The basic structure of cephalosporins (C15H21N3O7S) consists of a four-member beta-lactam ring. In cephalosporin, the ring is condensed with a six-member sulfur ring (the dihydrothiazine ring) (5). The substituent position 7 determines stability while the group at position 3 determines metabolic stability and pharmacokinetic characteristics (6).
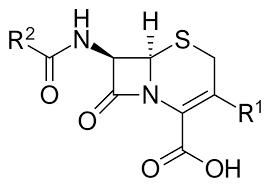
Figure 1. Basic structure of cephalosporin.
Cephalosporins work by interfering with the synthesis of peptidoglycan which is a major structural component of the bacterial cell wall (4). Carboxypeptidases, endopeptidases, and transpeptidases cross the cytoplasmic membrane and insert themselves into the cross-linked peptidoglycans. These enzymes are known as penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) and are the targets of beta-lactam medicines. The cephalosporin amide group is identical to the peptidoglycan pentapeptide. Cephalosporin attaches covalently to the PBPs, renders them inert, significantly compromises the structural integrity of the peptidoglycan, and kills the bacteria (4). In this study, we will virtually design a few derivatives of cephalosporins and use in silico techniques to evaluate their inhibitory potential against the PBP 4 complexed with the novel beta-lactam (FMZ) of H. influenza.
Materials and Methods
Hardware
The device used for the study was a personal laptop Device name: LAPTOP-KM8A50JS, Processor: AMD 3020e with Radeon Graphics, System type: 64-bit operating system x64-based processor.
Selection of Target Protein
The protein selected for the study bears a PDB ID: 3A3F. It is a crystal structure of PBP-4 from Haemophilus influenza, complexed with the novel beta-lactam (FMZ). The protein has a resolution of 2.10 Å with two chains i.e., chain A and chain B. There are 453 amino acids (total sequence length) and the organism is H. influenza.
Preparation of Protein
The crystal structure of the PBP-4 from H. influenza complexed with novel beta-lactam (FMZ) was downloaded in the PDB file format from the RSCB website (https://www.rcsb.org/). The Biovia Discovery Studio software was used to prepare the protein. Water molecules, hetero atoms, and chain B were removed from the protein. Polar hydrogens were added to the protein. The prepared protein was saved in the PDB file format. The 2D crystal structure of the prepared protein is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. The 2D crystal structure of the PBP-4 protein.
Identification of the Active Binding Site Coordinates
The original target protein complexed with FMZ was loaded into the PyRx virtual screening platform. First of all, chain B was removed from the scene. The prepared protein was also loaded onto the virtual screening platform. The amino acid residues which made up the original protein were revealed by expanding the protein. The position of the native ligand was identified and the 3D binding affinity grid box was adjusted to cover the entire active site residues. Following this, the original protein was removed from the scene.
Molecular Docking Simulation Studies
The compounds were loaded and their energy was minimized with the PyRx virtual tool. As we had already identified the active binding site, docking was executed. The results were saved as comma-separated values (CSV) files.
Bioavailability Study
SWISS ADME was used to study the Lipinski rule of 5 along with gastrointestinal (GI) absorption and blood-brain barrier permeant. The SMILE CODES of all the derivatives were uploaded and all the information displayed was copied to an MS Excel file. The purpose of this assessment was to find out whether the compounds follow the Lipinski rule of 5 (Molecular weight less than 500 Daltons, hydrogen bond donors less than 5, hydrogen bond acceptors no more than 10, Octanol-water partition coefficient/log P not greater than 5).
Toxicity Study
Toxicity analysis was done to assess the safety of a particular compound. It helps us to determine whether a compound or molecule, negatively impacts the normal biological function of an organism. OSIRIS Data warrior v5.5.0 was used for this process. The SMILES CODE of all the derivatives prepared was uploaded into the Data Warrior software, and each derivative was checked for mutagenicity, tumorigenicity, reproductive effective, and skin irritation. The toxic compounds were eliminated.

Figure 3. Chain A of the penicillin-binding protein with co-crystal ligand.
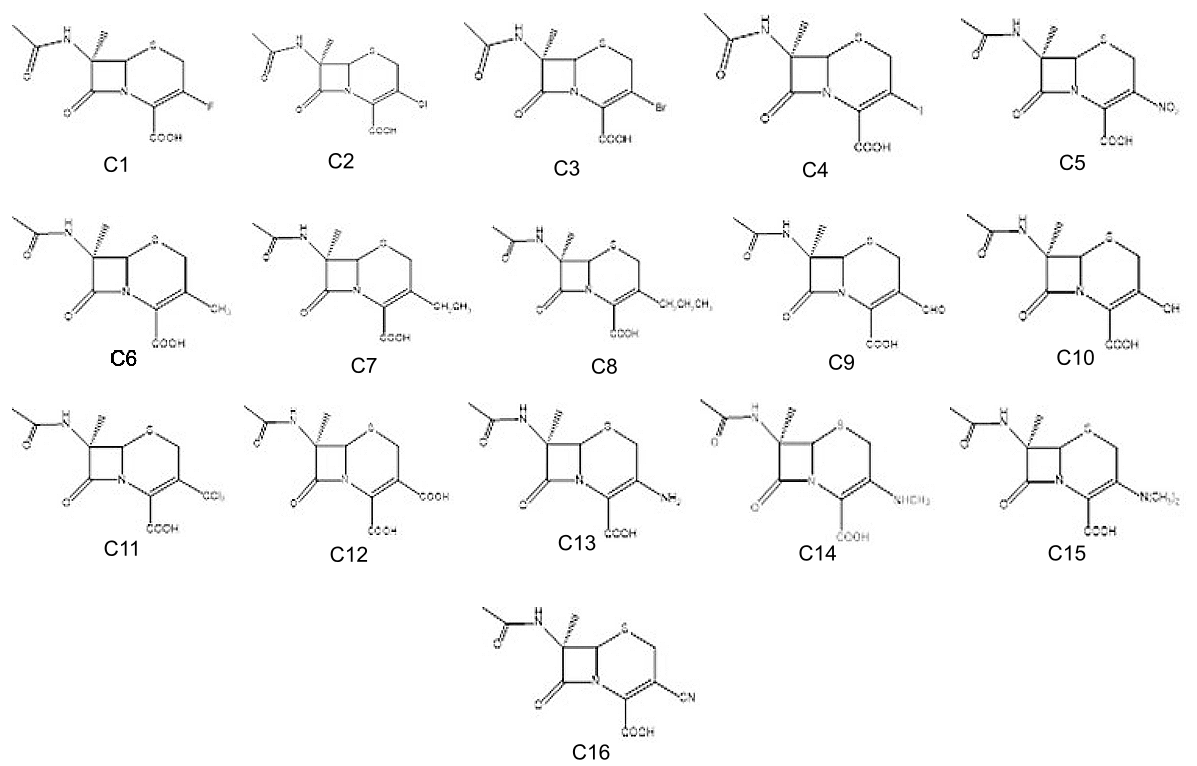
Figure 4. List of cephalosporin derivatives with their code.
Interactions Between the Cephalosporin Analogs and Protein
BIOVIA Discovery Studios Visualizer v21.1.0.20298 was opened and the prepared protein was loaded. The protein was defined as the receptor and the cephalosporin derivatives were defined as the ligand. The molecular interaction was observed in the form of a 2D diagram. The process was repeated for all the other derivatives.
Results
Target Protein and Cephalosporin Derivatives
The crystal structure of chain A of PBP protein was retrieved from the RCSB-PDB website, shown in Figure 3. Cephalosporins, like other beta-lactam medicines, work by interfering with the synthesis of peptidoglycan, which is a major structural component of the bacterial cell wall. Modifications in the molecule were made at the R3 position. A total of 17 Cephalosporin derivatives were prepared. The SMILES ID of all the compounds was generated with the Chem Draw Professionals 16.0 software. Their 2D chemical structures along with their respective compound code are listed in Figure 4.
Molecular Docking Simulation Study
Molecular docking is an efficient tool for in silico drug screening. To rate the binding potential of ligands to a protein, the PyRx tool can produce the binding affinity values (kcal/mol) for each ligand, and the binding potential of test ligands toward a protein can be ranked respectively by using the binding affinity of the native ligand as the benchmark. The binding affinity of the compounds is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. The binding energy of compound derivatives.
Compounds | Binding Affinity (kcal/mol) |
Cephalosporin | -7.4 |
Native ligand (FMZ) | -7.1 |
C1 | -7.4 |
C2 | -6.8 |
C3 | -6.2 |
C4 | -6.2 |
C5 | -6.9 |
C6 | -7.1 |
C7 | -6.4 |
C8 | -6.3 |
C9 | -6.3 |
C10 | -6.8 |
C11 | -5.8 |
C12 | -7.1 |
C13 | -6.3 |
C14 | -6.5 |
C15 | -5.8 |
C16 | -6.7 |
C17 | -6.3 |
Table 3. Swiss ADME against Lipinski’s rule of five.
Compounds | MW | #H-bond acceptors | #H-bond donors | GI absorption | BBB permeant | Lipinski #violations | Leadlikeness #violations |
C1 | 260.24 | 5 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C2 | 276.7 | 4 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C3 | 321.15 | 4 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C4 | 368.15 | 4 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 1 |
C5 | 287.25 | 6 | 2 | Low | No | 0 | 0 |
C6 | 286.26 | 4 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C7 | 267.26 | 4 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C8 | 270.26 | 4 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C9 | 257.27 | 5 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C10 | 271.29 | 5 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C11 | 285.32 | 4 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C12 | 258.25 | 6 | 3 | Low | No | 0 | 0 |
C 13 | 272.28 | 4 | 3 | Low | No | 0 | 0 |
C14 | 256.28 | 4 | 3 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C 15 | 270.3 | 4 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
C16 | 268.29 | 5 | 2 | Low | No | 0 | 0 |
C17 | 266.27 | 4 | 2 | High | No | 0 | 0 |
Preliminary ADME Study with Lipinski’s Rule
After determining the binding affinity of the cephalosporin derivatives, the ADME properties of the compounds were determined. Compounds that are active under in vitro settings can show lower activity under in vivo conditions due to poor ADME properties. Therefore, the bioavailability of a compound needs to be studied [9, 10]. Lipinski’s rule of five also known as Pfizer’s rule of five or rule of five is a rule of thumb to evaluate drug-likeness or to determine if the chemical compound with certain pharmacological or biological activity has chemical properties and physical properties that would make it a likely orally active drug in human.
The ADME properties of the cephalosporin derivatives are given in Table 3. All the compounds corroborate to specified parameters of Lipinski’s rule of 5. It is assumed that they will most likely be bioavailable. Since there were no Lipinski violations, therefore, the cephalosporin derivatives that were free from bioavailability issues were subjected to further studies.
Toxicity Analysis
Toxicity often leads to the withdrawal of drugs from clinical use (7). Data Warrior is a reliable software used by many researchers to predict the toxicity of compounds (8, 9). So, for the next step in designing the cephalosporin derivatives, we carried out an in silico toxicity study to determine the toxicity of the compounds. Out of 17 compounds, C2, C3, C4, C5, and C6 showed no signs of toxicity. The results of the toxicity analysis of the Cephalosporin derivatives are given in Table 4.
Binding Energy of Selected Compounds
After comparing the binding energy of the original cephalosporin and the native ligand with the Compounds, it was found that C1, C6, and C12 compound derivatives have a better binding affinity than cephalosporin and the native ligand. The binding energy comparison between the original cephalosporin, native ligand, C1, C6, and C12 is shown in Table 5.
Interaction of Compounds with Protein Target
Visualization of the 2D ligand interactions was done with the Discovery Studio Visualizer software. The summary of the ligand interactions of each compound with the amino acids of the proteins is shown in Table 6. The images of the 2D ligand interactions of the Compounds with protein are given in Figure 3.
Table 4. Toxicity analysis of 17 compounds.
Compounds | Mutagenicity | Carcinogenicity | Hepatotoxicity | Immunotoxicity | Cytotoxicity |
C1 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C2 | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
C3 | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
C4 | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
C5 | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
C6 | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
C7 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C8 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C9 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C10 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C11 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C12 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C13 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C14 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C15 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C16 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
C17 | Inactive | Inactive | Active | Active | Inactive |
Table 5. Binding energy comparison between cephalosporin, native ligand, and C1, C6, and C12.
Code | Binding energy (kcal/mol) |
Cephalosporin | -7.4 |
Native Ligand (FMZ) | -7.1 |
C1 | -7.4 |
C6 | -7.1 |
C12 | -7.1 |
Table 6. Summary of ligand interaction with the active sites of penicillin-binding protein.
Compound | Conventional Hydrogen bond | Other Interactive sites |
Cephalosporin | ILE159 (1.84 Å, 2.85 Å), SER423 (3.06 Å), LEU362 (2.20 Å) | ASN312 (3.79Å), SER69 (3.60Å) |
FMZ | ASP162 (2.41 Å, 2.48 Å), LEU362 (2.95 Å), LYS425 (2.00 Å) | PHE167 (5.07Å), LEU424 (5.37Å), ASP162 (3.41Å) |
C1 | ILE159 (2.10Å, 2.34Å), ASN168 (2.78Å) | ILE59 (4.93Å), LEU367 (3.44Å), LEU424 (4.33Å) |
C6 | ILE159 (2.15Å), ASN168 (2.78) | ILE159 (5.06Å), LEU362 (5.50Å), LEU424 (4.23Å), LEU424 (3.44Å) |
C12 | ASN168 (2.51Å), ARG364 (4.08), LYS425 (1.81Å, 2.73Å) | PHE167 (4.89Å), LEU362 (4.80Å) |

Figure 5. Visualization of 2D interaction of (A) cephalosporin, (B) native ligand, (C) compound 1, (D) compound 6, and (E) compound 12.
Discussion
Molecular docking is a computational technique to search for an appropriate ligand that fits both energetically and geometrically at the binding site of a protein. A more negative binding affinity value suggests a better binding between a compound and a protein. A low binding affinity value also indicates the low energy requirement for protein-ligand binding (11). Since the initial position has the highest binding affinity and the last pose has the lowest binding affinity to the target protein, the first pose is always regarded as the optimal pose. Out of all the cephalosporin derivatives, C1, C6, and C12 have shown a better binding affinity towards Chain A of the protein as compared to the binding affinity of the native ligand. C1 was found to have more binding affinity compared to the other 2 derivatives. In a toxicity study of the compounds, C1 was found to have toxicity for immunotoxicity and hepatoxicity, and C6 and C12 passed the toxicity. But still, we consider C1 for further study as we believe the benefit will outweigh the risks.
Nowadays, researchers use innovative research techniques that deviate from the conventional methods used to study synthetic drugs. To find promising synthetic compounds for the treatment of various diseases, in silico methods like molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations have been used more and more in drug discovery research (9, 12, 13-16). Some drugs, however, have a low oral bioavailability. Many researchers have chosen innovative drug delivery systems as the solution to the bioavailability problems related to drugs. Drug discovery and development processes have also used artificial intelligence, unsupervised machine learning, and supervised machine learning (11). Pharmaceutical researchers are utilizing novel methods in drug discovery programs as a result of scientific advancements. To identify a potent cephalosporin derivative against Haemophilus influenza, we have used the in silico methods that are affordable, safe, and sustainable.
Conclusions
The rate at which antibiotic resistance develops among bacterial species continues to increase due to the continued improper use of antibiotics and gene transfer among different species. To discover and develop new cephalosporins similar to the original cephalosporin, we designed and optimized various cephalosporins analogs using virtual screening and molecular docking analysis and compared them against cephalosporin and FMZ as the standard drugs. We identified some analogs that were good candidates and displayed better in silico activity against H. influenza. After analyzing all the parameters, including ADME properties, toxicity data, binding energy, drug-likeness, and drug score, cephalosporin with fluorine substitution at the 3rd position was identified as the best analog as this showed a good binding affinity with the target protein. In the future, the analog can be synthesized and evaluated for the in vitro activity to confirm the in silico antibacterial potency displayed by the compound.
Declarations
Ethics Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability
The unpublished data is available upon request to the corresponding author.
Funding Information
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicting interest.
References
- Jeśman C, Młudzik A, Cybulska M (2011) History of antibiotics and sulphonamides discoveries. Polski merkuriusz lekarski: organ Polskiego Towarzystwa Lekarskiego. 30(179):320–322.
- Akova M (2016) Epidemiology of antimicrobial resistance in bloodstream infections. Virulence 7(3):252–266.
- Mühlen S, Dersch P (2016) Anti-virulence Strategies to Target Bacterial Infections. Current topics in microbiology and immunology 398:147–183.
- Marshall WF, Blair JE (1999) The cephalosporins. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 74(2):187–195.
- Rodriguez R, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Blanca M (2005) Cephalosporin chemical reactivity and its immunological implications. Current opinion in allergy and clinical immunology 5(4):323–330.
- Elks J (1987) Structural formulae and nomenclature of the cephalosporin antibiotics. Drugs 34:240–246.
- Zothantluanga, JH, Aswin SK, Rudrapal M, Chetia D (2022) Antimalarial Flavonoid-Glycoside from Acacia pennata with Inhibitory Potential Against PfDHFR-TS: An In-silico Study. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry 12(4):4871–4887.
- Patowary L, Sarma M, Zothantluanga JH, Chetia D (2022) Repurposing of FDA Approved Drugs Having Structural Similarity to Artemisinin Against PfDHFR-TS Through Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies. Current Trends in Pharmaceutical Research 8(2):14–34.
- Zothantluanga JH (2021) Molecular docking simulation studies, toxicity study, bioactivity prediction, and structure-activity relationship reveal rutin as a potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3CL pro. Journal of Scientific Research 65: 96–104.
- Paul S, El Bethel Lalthavel Hmar JH, Zothantluanga HKS (2020) Essential oils: a review on their salient biological activities and major delivery strategies. Science Vision 20(2):54–71.
- Patowary L, Borthakur MS (2022) Computational studies of Bridelia retusa phytochemicals for the identification of promising molecules with inhibitory potential against the spike protein and papain-like protease of SARS-CoV-2. Sciences of Phytochemistry 1(1):29–41.
- Umar A, Zothantluanga JH, Aswin K, Maulana S, Sulaiman Zubair M, Lalhlenmawia H, Chetia D (2022) Antiviral phytocompounds “ellagic acid” and “(+)-sesamin” of Bridelia retusa identified as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 3CL pro using extensive molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation studies, binding free energy calculations, and bioactivity prediction. Structural Chemistry 33(3):1–21.
- Zothantluanga JH, Gogoi N, Shakya A, Chetia D, Lalthanzara H (2021) Computational guided identification of potential leads from Acacia pennata (L.) Willd. as inhibitors for cellular entry and viral replication of SARS-CoV-2. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 7(1):1–18.
- Khan J, Asoom LIA, Khan M, Chakrabartty I, Dandoti S, Rudrapal M, Zothantluanga JH (2021) Evolution of RNA viruses from SARS to SARS-CoV-2 and diagnostic techniques for COVID-19: A review. Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences 10(1):1–14.
- Pasala PK, Shaik RA, Rudrapal M, Khan J, Alaidarous M A, Khairnar SJ, Walode SG (2022) Cerebroprotective effect of aloe emodin: in silico and in vivo studies. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 29(2):998–1005.
- Umar AK, Zothantluanga JH (2021) Structure-Based Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics of Quercetin and Its Natural Derivatives as Potent Oxidative Stress Modulators in ROS-induced Cancer. Indonesian Journal of Pharmaceutics 3(2):60–71.
 ETFLIN
Notification
ETFLIN
Notification







