 ETFLIN
Notification
ETFLIN
Notification
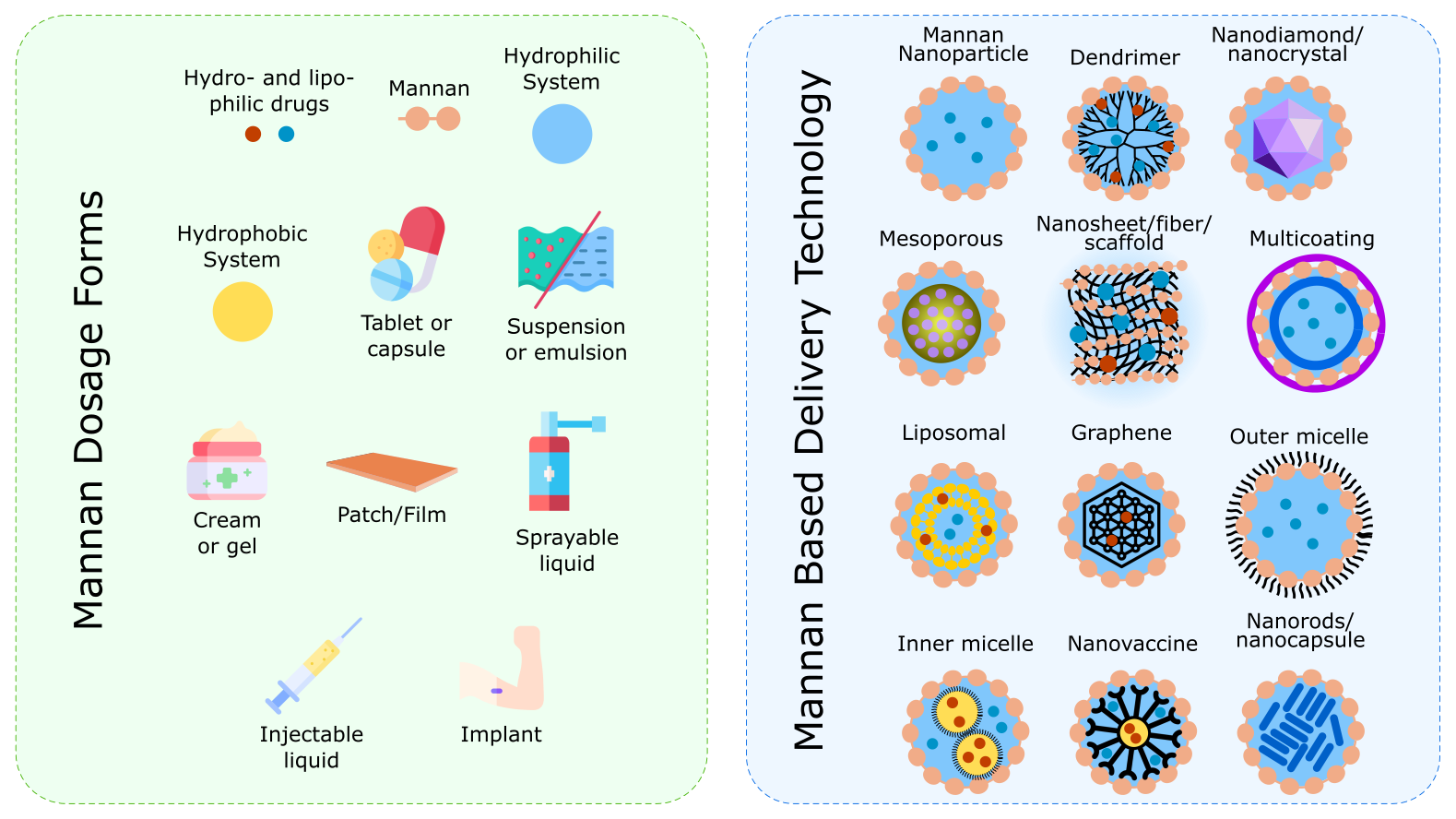
Mannan, a polysaccharide derived from various sources, has gained attention for its biocompatibility and potential in targeted drug delivery. Since its initial use in 1911 as an ointment base, mannan has been applied in cancer therapy, vaccine development, and as an antimicrobial agent. However, res...
More
Research Article
Open Access
Wednesday, 19 November 2025
Comparative Antioxidant and Antiradical Potentials of Four Curcuma species
by Alansheeja D. B. et al.

Research Article
Open Access
Monday, 10 November 2025
Differential Regulation of Slc40a1, Fth1, and Hmox1 by Deferasirox in Splenic Iron Overload
by Annisa Maharani Wibowo et al.

Research Article
Open Access
Monday, 10 November 2025
Evaluation of Antimicrobial Properties of Passiflora foetida Root Extract Sourced from Rehabilitated Coal Mining Sites in East Kalimantan
by Indah Woro Utami et al.

Research Article
Open Access
Friday, 7 November 2025
Hair Growth and Antibacterial Effects of Nanoparticle-Based Cosmeceutical Tonic from Pogostemon cablin and Morus alba Leaves
by Made Anindya Ayu Dyavaprathivi et al.
Research Article
Open Access
Thursday, 6 November 2025
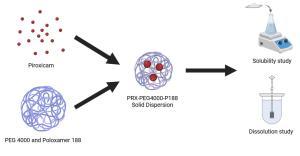
The Effect of Poloxamer 188 on the Solubility and Dissolution Behaviors of Piroxicam-PEG 4000 Solid Dispersions
by Adi Yugatama et al.
Research Article
Open Access
Thursday, 6 November 2025
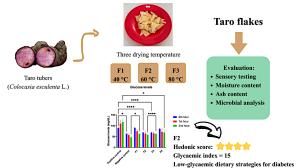
Low Glycemic Index Taro Tuber (Colocasia esculenta L.) Flakes as Alternative Food Product for Diabetes Management
by Asriana Sultan et al.

Research Article
Open Access
Wednesday, 5 November 2025
Self-Medication Practices among University Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by Steven Victoria Halim et al.

Research Article
Open Access
Saturday, 1 November 2025
Formulation and Stability Evaluation of Red Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus polyrhizus) Extract Gel
by Novi Febrianti et al.

Research Article
Open Access
Tuesday, 7 October 2025
Ethyl Acetate Fraction of Gynura procumbens Mitigates Hyperglycemia, Dyslipidemia, and Tissue Damage in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
by Yani Mulyani et al.

Research Article
Open Access
Tuesday, 7 October 2025
Web-Based Pharmacoinformatics Platform for Generic Drug Information in Gorontalo, Indonesia
by Mohamad Aprianto Paneo et al.

Research Article
Open Access
Wednesday, 23 July 2025
Reza Pratama et al.
MoreAbstract: Mannan, a polysaccharide derived from various sources, has gained attention for its biocompatibility and potential in targeted drug delivery. Since its initial use in 1911 as an ointment base, mannan has been applied in cancer therapy, vaccine development, and as an antimicrobial agent. However, research is still largely dominated by in vitro and preclinical studies, with few clinical trials conducted to date. This study aims to provide an overview of mannan's advancements, its uses in drug deli...

Research Article
Open Access
Monday, 30 June 2025
Desta Hutagaol et al.
MoreAbstract: Large pelagic fish such as tuna, skipjack, and mackerel are key export commodities for fishers at Bungus Oceanic Fishing Port due to high demand and their importance in processed fish products. This study analyzed trends, sustainable potential, and utilization levels of these resources in the western Sumatra Sea. Research conducted from March 17 to April 1, 2023, used a descriptive quantitative survey and literature review, with catch and effort data from 2015 to 2022 processed using Microsoft E...

Review
Open Access
Monday, 12 May 2025
Nur Rahmi Hidayati et al.
MoreAbstract: Diabetes mellitus is currently one of the global health threats. The prevalence and incidence of this disease continue to increase, both in industrialised and developing countries, including Indonesia. There are different types of DM marker gene polymorphisms in each racial group. These genetic variations contribute to the response of oral antidiabetic drugs. This article aims to conduct a narrative review of the influence of gene polymorphisms on oral antidiabetic drug response in patients with...

Public Insight
Open Access
Thursday, 13 February 2025
Munir Alinu Mulki et al.
MoreAbstract: Antibiotics are substances or compounds that are either synthetically produced or naturally generated by microorganisms, especially fungi. They are used as inhibitors of other microorganisms. The use of antibiotics in humans is based on their minimal toxicity to the human body. Inaccurate and prolonged use of antibiotics can lead to the development of resistance. A step taken to minimize antibiotic resistance is the introduction of the 2023 PITIK (Penyuluhan Informasi Tentang Antibiotik) program...

Research Article
Open Access
Friday, 27 December 2024
Ivan Ivanov et al.
MoreAbstract: This study focuses on the development of a chitosan-based hydrogel incorporating polyvinylpyrrolidone and polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride for the rehabilitation of damaged and contaminated skin. The thermal properties of chitosan-containing films were characterized by measuring the glass transition temperature (Tg) using differential scanning calorimetry. Due to challenges in accurately determining the Tg of chitosan from experimental and literature data, an additional method, dynamic ...
As a publisher, we create, store, and utilize cookies to enhance the features and services we provide. Several necessary cookies are implemented as part of the website's functionality.
_ga | etflin.com
The purpose of this cookie, set by Google Analytics, is to track the number of site visitors by remembering whether or not you have previously visited our website.
The following cookies are utilized to identify and authenticate users. By utilizing our service and registering an account within our system, you are consenting to the use of the following cookie. We do not share this data to any third party.
username | etflin.com
We employ this cookie to recognize users who have logged into the user system, ensuring that the data you manage is labeled with your username.
email | etflin.com
Email is utilized as our communication tool to send notifications, conduct initial registration verification, and account filtering.
name | etflin.com
We utilize your name to display on the website menu, indicating that you have successfully logged into the system.
token | etflin.com
We use a token to authenticate and identify your login session.
We Revolutionize Sciences, We Publish Sciences, We Are Scientist
ETFLIN